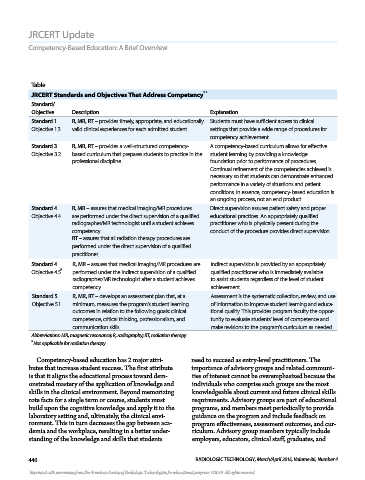
Page 138 - JRCERT Update Articles
P. 138
JRCERT Update
Assessment: Working Backward
Stephanie Eatmon, EdD, R.T.(R)(T), FASRT
eveloping a student learning assessment plan for accredited educational programs with input from the
for an imaging, radiation therapy, or medical medical imaging, radiation therapy, and medical dosim-
dosimetry program can be a daunting task. etry communities. The JRCERT Standards require
1-4
DStarting backward from the ideal graduate and programs to set goals and measure SLOs in 4 areas:
deciding what to measure makes the process easier and clinical competence, critical thinking, professionalism,
provides data essential for program improvement. By and communication. When working assessment back-
working backward, assessment becomes an exciting, ward, program faculty should consider these questions:
informative process. Examining the ideal graduate helps What skills, attitudes, and behaviors should our
identify skills, attitudes, behaviors, and values that are graduates possess in relation to the 4 goal areas?
important to measure. How will our graduates be differentiated from
Similar to terminology used in computer technol- graduates of other medical imaging, radiation ther-
ogy, the adage of “garbage in, garbage out” also is valid apy, and medical dosimetry educational programs?
for assessment. If the objectives and student learning How will we know whether our educational pro-
outcomes (SLOs) do not measure the skills, attitudes, gram has been successful?
behaviors, and values of the ideal graduate, no amount Answering these questions provides a more con-
of data or analysis will provide the program with crete idea of the assessment data needed to ensure the
information for continuous quality improvement. If program reaches its established goals. Each program
the ideal graduate is one who is skilled at producing a is unique, so its assessment plan will be unique as
PowerPoint (Microsoft) presentation, then that skill well. Although the 4 goal areas might be the same, the
should be measured. If that skill is not important for an objectives and SLOs differ depending on the type of
entry-level radiographer, magnetic resonance technolo- program, its structure, and degree offered. For exam-
gist, radiation therapist, or medical dosimetrist, then ple, at the certificate and associate degree levels, the
measuring that skill provides meaningless data and will program might not require students to write research
never lead to program improvement. This article pro- papers for publication; however, at the baccalaureate
vides a different lens through which to view assessment and master’s degree levels this might be appropriate.
and make the process easier and more useful to the One program might place extra emphasis on commu-
assessment team and the program. nication with patients from diverse populations, while
The Joint Review Committee on Education in another might focus on adaptability to new technolo-
Radiologic Technology (JRCERT) developed standards gies. The faculty for each program determine the
678 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY, July/August 2015, Volume 86, Number 6
Reprinted with permission from the American Society of Radiologic Technologists for educational purposes. ©2019. All rights reserved.